Tesla’s newly released 2024 annual impact report spans 42 pages and contains some remarkable insights about battery performance that should interest current and prospective EV owners. Document showcases data from over a decade of electric vehicle sales, providing unprecedented transparency about long-term battery health and upcoming efficiency improvements.
Tesla’s extensive dataset reveals patterns that weren’t fully understood when EVs first entered mainstream markets. With hundreds of thousands of vehicles now logging significant mileage, Tesla can present concrete evidence about how their battery technology performs over extended periods.
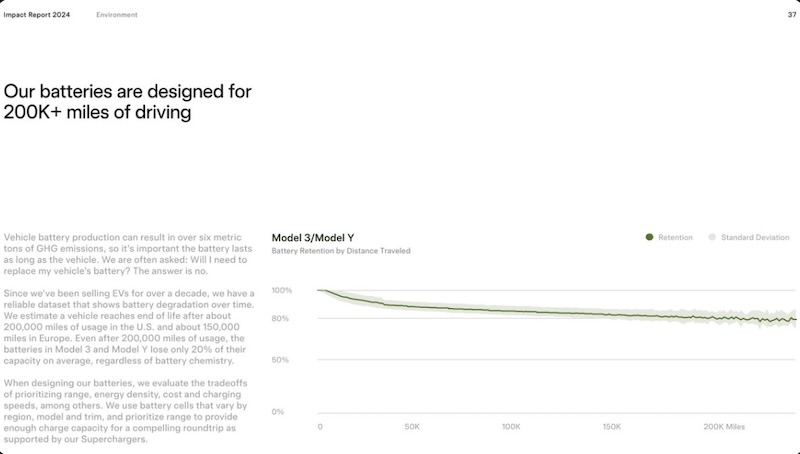
According to Tesla’s impact report findings, Model 3 and Model Y batteries retain approximately 80% of their original capacity after 200,000 miles of usage. Represents roughly 320,000 kilometers of driving for those using metric measurements. Degradation occurs regardless of battery chemistry, suggesting consistent performance across different cell configurations.
Tesla estimates that vehicles reach end-of-life status after about 200,000 miles in the United States and approximately 150,000 miles in Europe. However, these mileage thresholds don’t necessarily correlate with unusable battery capacity, as 80% retention still provides substantial range for most drivers.
The variance between U.S. and European end-of-life estimates reflects different driving patterns and usage scenarios. European drivers typically encounter more varied terrain and weather conditions, which can impact battery performance differently than American driving habits.
Tesla’s impact report notes that battery degradation accelerates during the initial 100,000 kilometers of operation, then stabilizes significantly. Pattern suggests that owners shouldn’t panic about early capacity losses, as the degradation curve flattens considerably after the initial period.
Perhaps the most intriguing revelation in Tesla’s impact report involves the upcoming Cybercab’s powertrain specifications. Tesla Robotaxi will utilize a next-generation platform delivering an estimated 5.5 miles per kilowatt-hour, representing a substantial improvement over current offerings.
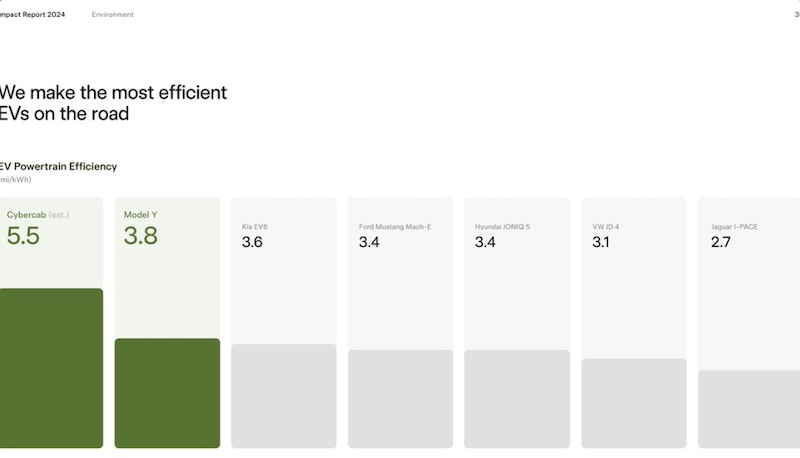
Tesla: “Cybercab will be built on our next-generation platform, which includes a new powertrain with an estimated 5.5 miles/kWh.”
For context, Model Y AWD currently achieves 3.8 miles per kWh under EPA testing conditions. Cybercab’s projected efficiency represents a 45% improvement, which could translate to significantly extended range or reduced battery requirements for equivalent performance.
The efficiency gains demonstrated in Tesla’s impact report raise questions about when this next-gen powertrain might appear in the company’s existing S3XY lineup. Such improvements could address range anxiety concerns while potentially reducing manufacturing costs through smaller battery pack requirements.
Tesla hasn’t provided timeline details for incorporating the new powertrain technology into existing models. However, the company’s history suggests that innovations typically migrate from flagship or specialty vehicles into mainstream offerings over time.
Interestingly, Tesla’s impact report shows slightly more conservative degradation figures compared to previous statements. Tesla previously claimed average degradation of around 15% at 320,000 kilometers, while current data suggests 20% capacity loss at similar mileage points.
Tesla Battery Degradation Patterns Show Resilience
This shift might reflect more comprehensive data collection or adjustments in measurement methodology. Real-world driving conditions often differ from controlled testing environments, potentially explaining the variance between earlier projections and current findings.
Most drivers don’t accumulate 320,000 kilometers during typical ownership periods, making the long-term degradation data more relevant for fleet operators or ride-sharing services. However, the information provides valuable insights for buyers concerned about resale values and long-term reliability.
Tesla’s impact report demonstrates that battery technology has matured significantly since early EV adoption periods. Data should reassure potential buyers who worry about expensive battery replacements within reasonable ownership timeframes.
The efficiency improvements promised for future vehicles suggest that Tesla continues pushing technological boundaries. Whether through improved chemistry, better thermal management, or enhanced power electronics, the company appears committed to advancing EV performance metrics.
Related Post
Tesla 2025.8.3 Update: New Battery Health Test Feature Gives Owners Unprecedented Transparency
Tesla Nevada LFP Battery Factory Nears Completion, Cuts China Dependence
Tesla Q2 2025 Deliveries: 384,122 Vehicles Beat Analyst Expectations, Production was 410,244
